Abstract
The oral micro-organism is an important factor for causing the oral disease with the host factor and environmental factors including the time factor for dental caries, periodontal disease as the main oral diseases, more over for elderly implant dental patients, who have frequently got the peri-implantitis [1]. So, many trials have been introduced to examine and to show the oral micro-organisms to let patients understand to control them effectively [2,3]. Traditionally, the culture method of the specific oral micro-organism has been used but hard for clinical use at the dental clinics because of the complexity of the process and time loss.
Introduction
The oral micro-organism is an important factor for causing the oral disease with the host factor and environmental factors including the time factor for dental caries, periodontal disease as the main oral diseases, more over for elderly implant dental patients, who have frequently got the peri-implantitis [1]. So, many trials have been introduced to examine and to show the oral micro-organisms to let patients understand to control them effectively [2,3]. Traditionally, the culture method of the specific oral micro-organism has been used but hard for clinical use at the dental clinics because of the complexity of the process and time loss. Phase contrast microscope has been used for many years for easy handling and showing the quantity and the motility of the oral micro-organisms classified by the morphological types. That has been very effective for the oral health education to clean and to keep the oral hygiene by motivating to control them, with use of the phase contrast microscope at the dental clinics [4]. Even though it is useful for micro-organism observation, there has been a disadvantage as impossible to configure out each oral microorganism individually except for using on the patient education. In recent years, gene analysis method as real time PCR has been developed for checking the quantitative findings for each oral micro-organism through dividing with each sort of individual oral micro-organism, with simple process at the dental clinic and by cooperation with the gene analysis specialists [5].
This paper showed the comparison and relation photos or the data for oral micro-organisms checked by real time PCR method as gene analysis and steel photo images for the phase-contrast microscope at the same dental implant patients, with relative 4 stages of the oral hygiene level as clean or rare, few, moderate and severe, in order to suggest the clinical guide-line for oral microorganism control.
Subjects and Method
4 cases were selected as relatively clean and rare for oral micro-organisms, a few, moderate and severe in quantitative analysis through the phase contrast microscopic findings from lots of the dental implant patients and then PCR test as gene analysis method was performed after mouth gaggle with easyperio mouth wash solution (Easygengagle, Easy-perio Co. Korea) solution. The expectorated solution was gathered into the capped bottle and delivered to the gene analysis company to analysis. Such 10 kinds of the oral micro-organisms as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (Aa) for relatively toxic micro-organism, Porphyromonas gingivalis (Pg) Tannerella forsythia (Tf), and Treponema denticola (Td) as the oral micro-organism related with the periodontal disease, Fusobacterium nocleatum (Fn), Prevotella intermedia (Pi), Prevotella nigrescens (Pn) and Parvimonas micra (Pm)as oral micro-organism related with the peri-implant inflammation and Streptococcus mutans (Sm) and group of Streptococci(St) as the oral micro-organism which related with causing the dental caries were checked by use of gene analysis PCR method. The total amounts of the oral micro-organisms were checked with the estimated numbers. The results have been replied back within two days later and compared with the photo image from the phase contrast microscope with the same dental implant patient.
Results
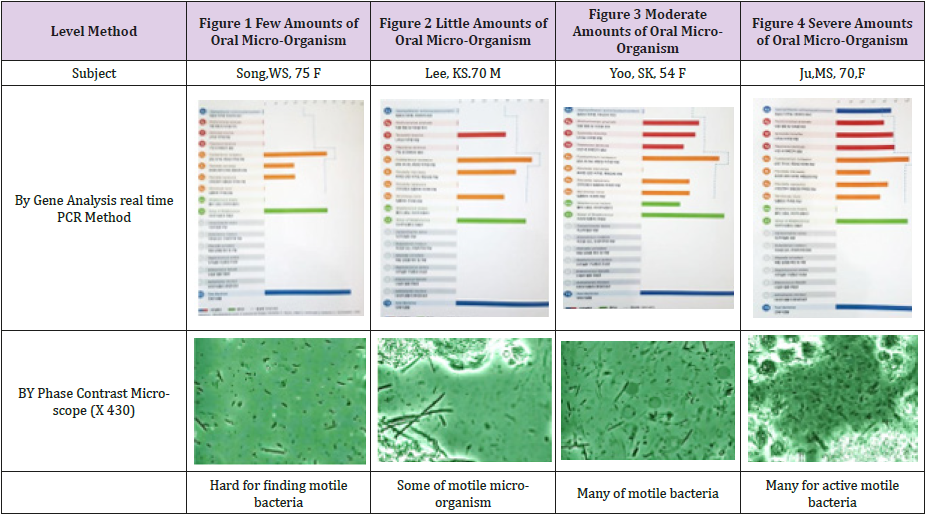
Table 1: ~4 4 cases of the oral micro-organisms examined by PCR gene analysis method and by use of the phase contrast microscope.
The PCR graphic images and the photos of the oral microorganisms observed with the phase-contrast microscope at 4 cases classified with 4 stages as few, little, moderate and severe amounts of oral micro-organisms for dental implant patients with more than 4 teeth, were shown in figures in Table 1. It showed relatively relationship between two figures as the results graphics by gene analysis PCR method and the image for the oral micro-organisms observed by the phase contrast microscope, classified according to the level of the amounts of the bacteria.
Discussion
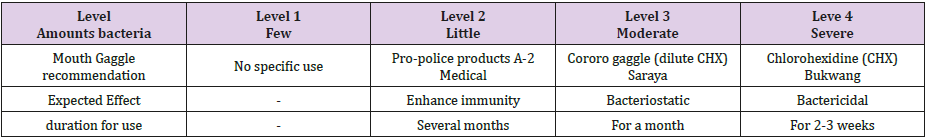
Until recent years, the phase contrast microscope has been used to examine the oral micro-organisms with alive and motile state classified with their morphology as cocci, bacillus, filamentous and spiral type, and it has been effective for oral hygiene education for dental patient [6]. It should be important to solve the problems for micro-organisms control, as well as to find the oral microorganisms which the implant patient had. The general way to control the oral micro-organisms would be to use the mouth gaggle solution for certain period, although such physiological method as tooth-brushing, professional mechanical tooth cleansing, use the dental floss or interdental brush and irrigation with the water pik would be recommended for maintaining the oral micro-organisms after control for valancing each bacteria environment [7]. Table 2 shows the one of the recommendable guidelines to use the mouth rinse solution to control the oral bacteria, after receiving the results paper for PCR analysis for dental implant patients, at the dental clinics.
Table 2: Recommendation of the mouth gaggle solution according to the level of the oral micro-organism for dental implant patients.
Conclusion
The oral micro-organism control for dental implant patients should be very important in order to prolong the dental implant life as well as to enhance the oral hygiene ability for the dental patients. The clinical use of the clinical investigation of the oral micro-organisms by use of the gene analysis Real time PCR method was useful for consulting and prescription of the proper gaggle solution according to amounts level of the oral bacteria individually and the phase contrast microscope was useful for oral hygiene education to give them a motivation to control of excessive amounts of the bacteria or maintain the balanced oral micro-organism environment after control, for dental implant patients in clinical.
References
- Jung KY, Chang YS, Lee YJ, Woo SH (2008) Correlation Coefficient between the amounts and the motile of various Oral Micro-organism. Int J Clin Prev Dent 4(3): 168-176.
- Chang YS, Jung MA, Shin SC (2008) Evaluation of Motility and Distribution of Oral Microflora in Koreans using the Phase Contrast Microscope. Int J Clin Prev Dent 4(1): 28-39.
- Paik DI, Shin SC, Park YD (2011) Clinical Preventive Dentistry (5th ). KoMunSa Seoul pp. 279-288.
- Listgarten MA, Schifter C (1982) Differential Dark field microscopy ofsubgingivalbacteria as an aid inselectingrecall intervals; results after18 months. J Clin Periodontol 9(4): 305-316.
- Hang KS, Cho JW (2017) Reliability of Quantitative Analysis of Bacteria Causing Perioodontal Disease by MRT-PCR. Int J Clin Prev Dent 13(2): 73-80.
- Chang YS (2019) The control plan of the oral micro-organisms for the dental implant patient through the gene analysis examination system. Int J Clin Prev Dent 15(2): 77-81.
- Kim SH, Lee K H, Jwa SK (2015) Change in Oral Microflora with Oral Gargling and Interdental Brushing. Int J Clin Prev Dent 11(3): 143-152.

 Case Report
Case Report