Abstract
Background: The management of metastatic colon cancer represents an oncologic challenge. The treatment strategy for patients with such an advanced tumor situation is not clearly defined. Accordingly, major surgical treatment as the indispensable part of a multimodal treatment can offer cure in such patients. The implementation of robotic surgery, in the field of surgical oncology, offers great advantages in terms of surgical quality and quality of life.
Methods: We present a unique case of right-sided colon cancer with synchronous hepatic metastasis, which has been treated by means of robotic right hemicolectomy using complete mesocolic excision and synchronous left hemihepatectomy. The clinical, histopathological criteria, the surgical and systemic therapy were investigated.
Results: A 60-year-old female was presented with abdominal pain in the right hemiabdomen and at the same time a tumor mass in the right hemicolon and multiple hepatic metastases were detected. Pathological evaluation of the core needle biopsy from the primary tumor mass confirmed adenocarcinoma. After primary neoadjuvant systemic treatment with chemotherapy and because of partial response, the indication for combined, synchronous colon and liver resection was given. Major surgical treatment, including right hemicolectomy with Complete Mesocolic Excision (CME) and left hemihepatectomy was performed. The histopathological examination showed a R0- resection. The patient recovered from the surgery without postoperative complications and was discharged eight days after surgery.
Conclusion: This unique case demonstrates that patients in good general conditions with advanced metastatic colon cancer benefit from multimodal treatment, considering major surgery as the important part of this concept, offering a chance for cure. Through the use of the advantages of robotic surgery in terms of precise surgical technique and minimal operative trauma, several positive aspects such as individualized tumor treatment of highest quality, fast recovery from major surgery and quality of life can be combined.
Keywords: Robotic Surgery; Colectomy; CME; Hepatectomy; Liver Metastasis; Liver; Colon Cancer
Introduction
After successful implementation of minimally invasive surgery in the field of surgical oncology -especially for malignant disorders of the liver and the colon- [1-11], robotic surgery gains more attention and acceptance in everyday practice [9,10,12,13-15]. Through further development on technical and surgical aspects, the indication spectrum has been expanded, involving more complex situations such as major hepatic resections. These can be safely performed with minimal blood loss, faster convalescence and better quality of life in terms of postoperative and chronic pain, while oncologic outcome is like open procedures [5-9,12,13]. A further advantage in case of robotic liver resection represents the technical advantages offered by this modality: precise and meticulous dissection of tissue and vessels, better visualization -through a highperformance three-dimensional, high definition vision system- in comparison to conventional laparoscopic procedures and better options for troubleshooting through translation of the surgeon’s hand movements into more precise movements of the EndoWrist instruments, when major sewing is needed [9,10].
Furthermore, in the field of robotic colorectal surgery there is also a great progress in terms of surgical technique. Nowadays it is possible to achieve highest surgical quality in terms of Complete Mesocolic Excision (CME) when using the robotic system [11]. Considering these, patients with advanced tumor situations can benefit from the implementation of robotic surgery as integral part of a multimodal oncological treatment.
Here, we present a unique case of advanced metastatic colon cancer that was treated successfully by a robotic major surgical procedure, combining right hemicolectomy with CME and left hemihepatectomy simultaneously.
Case Report
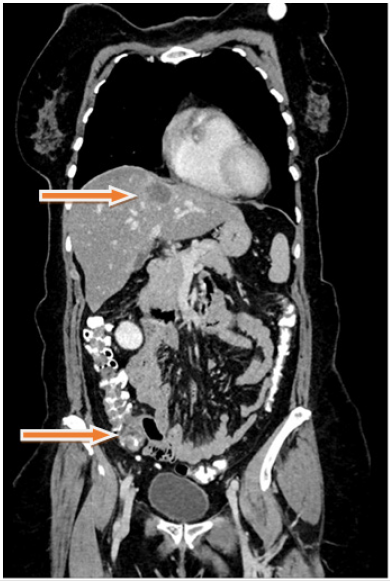
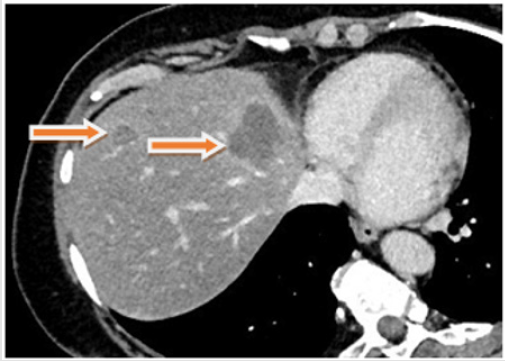
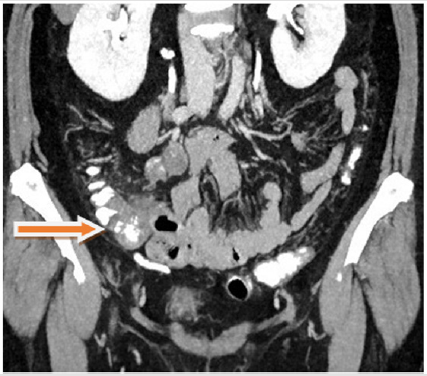
Figure 1: CT at time of reevaluation after systemic chemotherapy showing the liver metastases and the the primary tumor in the right hemicolon (arrows).
A 60-year-old female patient with an advanced right sided colon cancer with synchronous multiple liver metastases was admitted to the University Clinic for General, Visceral, Vascular and Transplant Surgery, University of Magdeburg, for surgical evaluation after administration of palliative, systemic chemotherapy combining leucovorin calcium (folinic acid), 5FU and irinotecan hydrochloride (FOLFIRI) and Bevacicumab over six months. After performing a computed tomography (CT, Figures 1-3) and complementary diagnostics through Magnet-Resonance Imaging (MRI) there was a partial response of the primary tumor mass in the right hemicolon and of the multiple liver metastases, which were finally located in the left liver lobe. After thorough examination of all oncologic aspects in our interdisciplinary tumor conference and due to partial response after systemic chemotherapy and the good general condition of the patient we decided for robotic right hemicolectomy and left hemihepatectomy simultaneously.
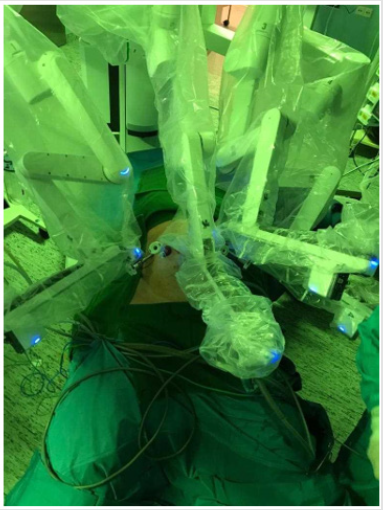
The robotic resection for colon and liver was performed using the “da Vinci robotic X system” (Intuitive Surgical, Inc., CA, USA) in an already described fashion [9-11]. We initiated the procedure with the left hemihepatectomy. Therefore, the robot was initially docked coming from the patient’s right shoulder, while the trocars were placed in the left and right upper abdomen (Figures 4 & 5). During the exploration of the abdomen intraoperative ultrasound was used, in order to determine the extent of liver metastasis, to exclude further lesions in the right liver lobe and to define the resection margins. After successful dissection of the hilar structures, identification of the left sided main vessels (left hepatic artery and left branch of the portal vein), parenchyma dissection was performed using several tissue dissecting devices such as the harmonic. During left hemihepatectomy there was a low blood loss (250 ml) without need for Pringle maneuver. After successful liver resection, we redocked the robotic system in order to proceed with the right hemicolectomy. Docking position and surgical technique including robotic right hemicolectomy, CME and Central Vascular Ligation (CVL) have been described recently [11].
Figure 5: Docking of the da Vinci robotic X system (Intuitive Surgical, Inc., CA, USA) for robotic hemi hepatectomy.
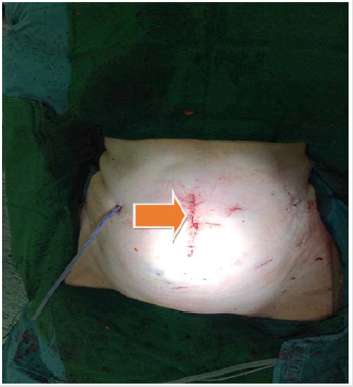
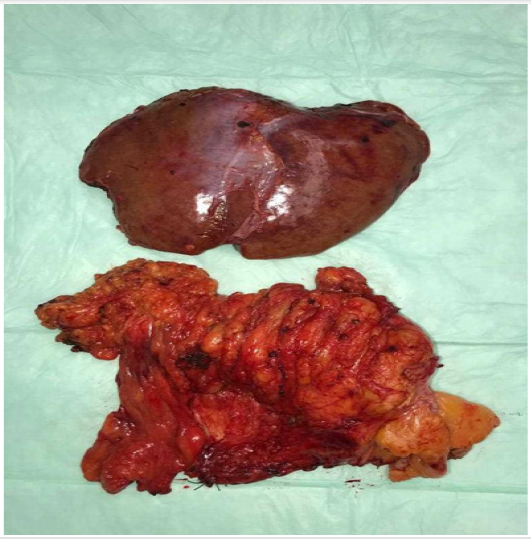
The removal of specimens took place in a fashion similar to conventional laparoscopy by using a small incision in the middle line (Figure 6). The final histopathological examination of both specimens showed a R0- resection (Figure 7). The duration of stay in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) was one day and overall there were no signs of a disorder of renal or hepatic function or other postoperative complications. The patient recovered from this major surgical procedure and was discharged after eight days of an unremarkable postoperative course.
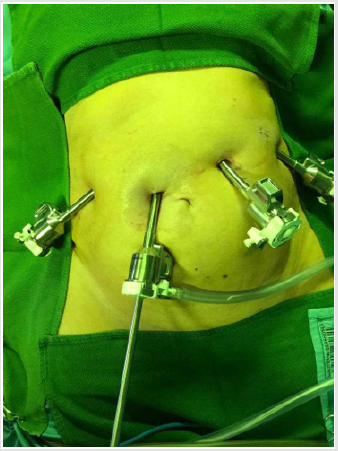
Figure 6: postoperative outcome after surgery and retrieval of both specimens through a small incision in the middle line (arrow).
Figure 7: Surgical specimens after left hemihepatectomy and synchronous right hemicolectomy using the technique of complete mesocolic excision (CME).
Discussion
Since the first efforts using the robotic surgical system, the number and complexity of robotic surgical procedures have been worldwide rapidly increasing [9-15]. Especially in the field of surgical oncology the technical improvements are astonishing. In this fashion, it is possible nowadays to perform a colon resection with CME with excellent oncological outcome in terms of specimen quality by preserving the mesocolic plane [11], exactly as described by Hohenberger et al. but for open surgery- [16]. Even in terms of hepatobiliary surgery, the most complex surgical field when performed minimally invasive, the robotic procedures are gaining much more importance comparing to conventional laparoscopic techniques by possessing essential advantages such as flexible movements, a better vision and improved modalities for troubleshooting and avoidance of conversion [10]. In a recently published international consensus statement [14] the authors underline the above-mentioned technical advantages of the robotic liver resection. They also state that there is evidence for the robotic hepatectomy to be safe and feasible as conventional hepatectomy and to have similar oncologic outcomes, when compared to open and conventional laparoscopic procedures [14].
Furthermore, the robotic procedures seem to provide less blood loss during resection, faster convalescence after surgery and lower morbidity when compared to open procedures [14]. When compared with conventional laparoscopic liver resection there are no significant differences in the above-mentioned parameters. Overall the robotic procedures combine several technical advantages in comparison to the conventional laparoscopic methods. That is the reason, why liver surgeons, using the robotic systems are expanding their indication for its use [14]. On the other hand, operating times for the robotic procedure are significantly longer and the setting of robotic surgery provides higher costs. Furthermore, robotic surgical procedures have to be performed by experienced surgeons [14]. Due to last point several training programs have been initiated in order to optimize the learning curves [12,13].
In terms of synchronous robotic surgery for colon and liver there is no evidence except for case series considering robotic colectomy combined with minor liver resection [15]. In this series the authors are indicating that this procedure is safe, feasible and provides several advantages for the patients [15]. We reported a unique case, where major liver and colon resection were performed simultaneously. Based on our experience, patients have a benefit by means of the advantages offered by robotic surgery. Although the current evidence for advanced robotic surgery is generally weak, we firmly believe that the indication for major robotic surgical procedures should be given in young, stable patients in a good general health status. Long term oncological outcomes, possible ways for reducing costs and long operating times are matters, which need further investigation.
Compliance with ethical standards: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the University Hospital Magdeburg and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Buell JF, Cherqui D, Geller DA, O'Rourke N, Iannitti D, et al. (2009) The international position on laparoscopic liver surgery: the Louisville Statement, 2008. Ann Surg 250(5): 825-830.
- Gigot JF, Glineur D, Santiago Azagra J, Goergen M, Ceuterick M, et al. (2002) Laparoscopic liver resection for malignant liver tumors: preliminary results of a multicenter European study. Ann Surg 236(1): 90-97.
- Belli G, Gayet B, Han HS, Wakabayashi G, Kim KH, et al. (2013) Laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy a consideration for acceptance as standard of care. Surg Endosc 27(8): 2721-2726.
- Wakabayashi G, Cherqui D, Geller DA, Buell JF, Kaneko H, et al. (2015) Recommendations for laparoscopic liver resection: a report from the second international consensus conference held in Morioka. Ann Surg 261(4): 619-629.
- Gayet B, Cavaliere D, Vibert E, Perniceni T, Levard H, et al. (2007) Totally laparoscopic right hepatectomy. Am J Surg 194(5): 685-689.
- Ishizawa T, Gumbs AA, Kokudo N, Gayet B (2012) Laparoscopic segmentectomy of the liver: from segment I to VIII. Ann Surg 256(6): 959-964.
- Gumbs AA, Gayet B (2007) Totally laparoscopic left hepatectomy. Surg Endosc 21(7): 1221.
- Gumbs AA, Gayet B (2008) Totally laparoscopic central hepatectomy. J Gastrointest Surg 12(7):1153.
- Croner RS, A Perrakis, M Brunner, KE Matzel, W Hohenberger, et al. (2015) Pioneering robotic liver surgery in Germany: first experiences with liver malignancies. Front Surg 2: 18.
- Croner RS, Perrakis A, Hohenberger W, Brunner M (2016) Robotic liver surgery for minor hepatic resections: a comparison with laparoscopic and open standard procedures. Langenbeck Arch Surg 401(5): 707-714.
- Croner RS (2018) Robotic complete mesocolic excision in right hemicolectomy - a video vignette. Colorectal Dis 20(7): 648-649.
- Chen PD, Wu CY, Hu RH, Chen CN, Yuan RH, et al (2017) Robotic major hepatectomy: Is there a learning curve? Surgery 161(3): 642-649.
- Choi GH, Chong JU, Han DH, Choi JS, Lee WJ (2017) Robotic hepatectomy: the Korean experience and perspective. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 6(4): 230-238.
- Liu R, Wakabayashi G, Kim HJ, Choi GH, Yiengpruksawan A, et al. (2019) International consensus statement on robotic hepatectomy surgery in 2018. World J Gastroenterol. 28 25(12): 1432-1444.
- Dwyer RH, Scheidt MJ, Marshall JS, Tsoraides SS (2018) Safety and efficacy of synchronous robotic surgery for colorectal cancer with liver metastases. J Robot Surg 12(4): 603-606.
- Hohenberger W, Weber K, Matzel K, Papadopoulos T, Merkel S (2009) Standardized surgery for colonic cancer: complete mesocolic excision and central ligation-technical notes and outcome. Color Dis 11:354-364.

 Case Report
Case Report