Abstract
To study effect of сomplex therapy and nebivololi on parameters of ventilationperfusion function of lang and parameters of diastolic function right ventricle of heard in patients with bronchial asthma complicated by pulmonale hypertension failure.
Introduction
In recent decades, an increase in the prevalence and mortality of patients with severe bronchial asthma (BA) with pulmonary hypertension (PH) has been observed [1-3]. Severe BA is one of the causes of LH and accounts for more than 50% in the structure of the formation of pulmonary arterial hypertension (AH) of chronic pulmonary heart [4,5]. Chronic pulmonary hypertension is a serious complication of a number of chronic lung and heart diseases. In addition to vasoconstriction, its pathogenesis includes injury to the peripheral pulmonary arteries leading to their structural remodeling. Increased pulmonary vascular synthesis of an endogenous vasodilator, nitric oxide (NO), opposes excessive increases of intravascular pressure during acute pulmonary vasoconstriction and chronic pulmonary hypertension, although evidence for reduced NO activity in pulmonary hypertension has also been presented. NO can modulate the degree of vascular injury and subsequent fibroproduction, which both underlie the development of chronic pulmonary hypertension [6].
Nitrogen preparations, ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, beta-blockers and ozone therapy (OT) against the background of basic treatment are used as correctors of the impaired function of the cardiorespiratory system [7,8]. According to A.G. Chuchalin, V.S. Zadionchenko, A.M. Shchikota, I.V. Pogonchenkova, and others, the mechanism of development of PH and remodeling of the right ventricle of the heart in patients with chronic pulmonary heart is still unclear. The main criteria for early diagnosis and prediction of pulmonary heart development in patients with COPD and severe BA have not been developed [9,10]. According to literature data, Uzbekistan has not developed optimal regimens for the prevention and treatment of patients with PH, taking into account the peculiarities of the course of BA.
Purpose of the Study
To study the state of the ventilation and perfusion ability of the lungs (VAL), pulmonary hemodynamics and right ventricular diastolic function (RVDF) in the dynamics of complex treatment with nebivolol in patients with BA with PH.
Material and Research Methods
34 patients with asthma with pulmonary hypertension and 20 healthy individuals were examined (mean pulmonary arterial pressure – PAP mn >25 mmHg). All patients received the procedure daily for 10 days. According to the method of treatment, patients are divided into 3 groups: I gr. - 20 patients received basic therapy (BT) according to (GINA 2011); Gr. - 11 patients received BT, nebivolol in a dose (5-10 mg / day); III gr. - 12 patients received BT and OT (intravenous administration of ozone-oxygen mixture in physical solution, 1000 mg / l). VAL was determined on the Medikor apparatus, the following parameters were measured: forced expiratory volume per 1 sec (FEV1), lung capacity (LC) and Tiffno index (FEV1 / VC), Blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) was determined by pulse oximetry. Doppler Echocardiography investigated: the ratio of early and late diastolic filling (E / A), isovolumic relaxation time (IRT, m / s), the deceleration time of the maximum speed of early diastolic filling (DT, m / s), atrial content fraction (ACF, %) and the level of mean pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP mn, mm Hg). The results are processed using the Excel software package, using t - Student’s criterion. Differences between the studied parameters were recognized as reliable at p <0.05.
Research Results
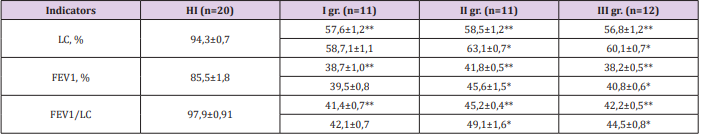
According to the VAL, there was a decrease in the ventilation-perfusion state of the bronchopulmonary system in all patients with PH. Thus, the FEV1 index in the 1a subgroup was 38.2 ± 0.5%, in 2a -46.1 ± 1.6%, (p <0.005), SaO2, respectively, in 1a - 85.1 ± 5% and in 2a 89.6 ± 1.4% (p <0.05), which is typical for the increase in bronchial obstruction. When conducting EchoCG, there was a significant increase in DT and IRT, and the E / A ratio was 0.93 ± 0.04 (p <0.05 compared with 1.61 ± 0.02 KG). Analysis of VAL indicators in the dynamics of treatment showed a significant increase in indicators in the II and III groups of patients (Table 1). LC gain; FEV1 and Tiffno index in II gr. after treatment, increased by 8.4, respectively; 9.1 and 8.7%, in III gr. by 5.9; 6.8 and 5.4% (p <0.05), and in I gr. increase in indicators is not significant (p> 0.05). Note: in the numerator, the indicators are before treatment (significance of difference with indicators of HI), in the denominator - after treatment (reliability of difference with indicators before treatment): ** p <0.005; * p <0.05.
Table 1: VAL indicators in patients with BA with pulmonary hypertension in the dynamics of various regimens, (M±m).
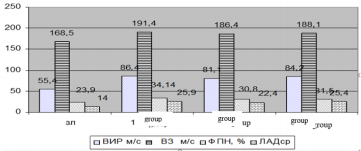
In our study, the use of nebivolol on the background of BT in patients with BA with PH led not only to a decrease in PAPmn, but was also accompanied by a positive shift in pulmonary hemodynamics, DF RV (Figure 1). After complex treatment, IRT decreased in the II and III groups of patients, respectively, by 10.5% (p <0.01) and 5.1% (p <0.05). PAPmn after treatment in the II-nd and III-nd groups in patients decreased respectively 15.7 and 9.5%, the reliability of the difference with the Figure 1 before treatment (p <0.05).
Note: ВИРм\с – IVR m/s ВЗ м\с – DT m\s ЛАДср - PAPmn ФПН – ACF
Figure 1: Effects of various treatment regimens on hemodynamic parameters and RVDF in patients with asthma with pulmonary hypertension.
Discussion
The decrease in the indices of filling in the early diastole found by us should be explained by the disturbance of relaxation of the hypertrophied right ventricular (RV) myocardium, as a result of which the decrease in intraventricular filling slows down and the ACF increases. It should be noted that in patients with BA with PH, the structure of RV filling in diastole changes. The mutual complication of disorders in combination with cardiorespiratory pathology is based on the commonality of some pathogenesis links - impaired pulmonary and cardiac microcirculation, the development of hypoxemia and pulmonary hypertension [5,6]. It was found that in patients with BA with PH receiving nebivolol and ozone therapy on the background of BT, there is a decrease in the early atrioventricular gradient, improved RVDF, pulmonary hemodynamics, and lung ventilation capacity.
Conclusion
a. The relationship between the severity of the clinical course of BA, a decrease in FEV1 and an increase in PAPmn (p <0.05) was determined.
b. In the dynamics of complex treatment with nebivolol of BA patients with pulmonary hypertension, the blood saturation with oxygen increases, PAPmn decreases and RVDF indices improve (p <0.05).
c. Comprehensive treatment of patients with asthma with pulmonary hypertension improves the ventilation and perfusion capacity of the lungs and simultaneously reduces the tone of the pulmonary vessels.
References
- Alyavi АL, Aripov BS, Abdullaev АKh, Sadikova GА, rakhimova DА, et al. (2016) Functional interrelations of the parameters of peripheral blood circulation and respiratory system during the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Compilation scientific tr Tashkent 322.
- Alyavi АL, Rakhimova DА, Sabirjanova ZТ (2016) Pulmonary hypertension/Monograph. Tashkent 89.
- Rakhimova DA, Kasimova (2012) GM Estimation of psychovegetative factors of regulation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonale diseases. Journal of life-sciences Argentina №4: 457-461.
- Alyavi АL, Sadikova GА, Rakhimova DА, Sabirjanova ZТ (2016) Stage rehabilitation of diseases of the cardiorespiratory system/Monoglraph. Tashkent 68.
- Drovyannikova LP (2014) Possibilities of drug therapy in patients with bronchial asthma Nat. congress on BOD. Com М1483: 389.
- Hampl V, Herget J (2000) Role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of chronic pulmonary hypertension. Physiol Rev 80(4): 1337-1372.
- Zadionchenko VS, Shchikota AM, Pogonchenkova IV (2014) Correction of endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic pulmonary heart cardioselective β-adrenergic blockers Rus med Journal № 4: p.285-289.
- (2018) Ministry of health of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
- Chuchalin АG (2017) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease М 1: 89.
- Weitzenblum E, Chaouat A (2009) Cor pulmonale. Chron Respir Dis 6(3): 177-185.

 Review Article
Review Article