Impact Factor : 0.548
- NLM ID: 101723284
- OCoLC: 999826537
- LCCN: 2017202541
Dao Chanh Thuc*
Received: August 19, 2018; Published: August 29, 2018
*Corresponding author: Dao Chanh Thuc, Physical Education Department, A Giang University, Vietnam
DOI: 10.26717/BJSTR.2018.08.001661
Purpose: study of peculiarities of heart rate variability system in excellent athletes with different level of stress resistance. Material: 22 excellent athletes, members of the Vietnamese National Team Karate in the research. The level of stress resistance (stress tolerance) was determined by the results of test called "Stress Test” The athletes were divided in two groups according to level of stress resistance. Were used the cardiac monitor «Polar RS800CX» for studied of heart rate variability. Results: It revealed the increasing of level of stress resistance related with improving the system of autonomic regulation of heart rate in excellent athletes. This reflected by relaxation of level of tension and activation of parasympathetic part of autonomous nervous system. Were revealed the bigger meanings of LF/HF in athletes with average level of stress resistance for concerning to athletes of high level of stress resistance indicates the amplification of sympathetic and weakening of parasympathetic link of autonomic nervous system [1]. The athletes with high stress resistance level has high of level of heart rate variability and low of centralization of heart rate regulation for compared to athletes with average level of stress resistance.
The stress tolerance is one of the main characteristics of athletes which manifested during psychoemotional load with related of competition activity [1-3]. Stress tolerance links with the complex of adaptation reaction of organism of athletes which directed to overcoming the negative effects of external stimuli of psychosomatic tension [4]. Among different mechanisms which use for coping of stress reaction in excellent athletes one of the ways is mobilization of physiological reserves which dilution of negative influences of external factors [5-7]. We can't prevent of influence from stress factors to athletes in sport activity but needed find of optimal way which can minimization of stress influence in competition condition [4,8-10]. In modern excellent sport the manifestation of emotional stress accompanied by mobilization of different physiological systems for the aim of forming of functional system which provides of stress resistance in athletes [6,11,12].
The psycho-emotional factors are links of activity with difference levels of adaptation reactions of organism of excellent athletes [6,1]. One of the important systems of the vegetative support of muscular and psycho-emotional activity of athlete is cardiovascular system [1]. According to the conception of RM Baevsky the changes of cardiovascular system is indicator of adaptation reactions of organism of athletes (Baevsky, 2004). The observed dynamics of prompt adaptation reactions in intensive muscular activity were proposed by the classification RM Baevsky [11] for evaluating functional state of the body according to the degree of regulatory systems tension which makes use of four scales.
The first scale is the state of partial adaptation characterized by a minimum tension of regulatory systems. The second scale is the functional tension state which corresponds to the period of stabilization of functioning of organism of athletes [1]. The third scale, the state of overstrain, is characterized by the exhaustion of the reserve potentialities of functional system which shows up in a substantial increase in risk of stress disorders. Thus, for possibilities of management of psychophysiological states of athletes in stress situation the study of stress resistance will can use for optimization of pre-competition and other conditions [1]. The purpose of the work: study of peculiarities of heart rate variability system in excellent athletes with different level of stress resistance.
22 excellent athletes, members of the Viet Nam National Team Karate wrestling took part in the research. The level of stress resistance (stress tolerance) was determined by the results of test called "Stress Test" with analysis of information in adopted mode. This method is included in apparatus-program psychodiagnostic complex «Multipsychometr -05» [13] The athletes were divided in two groups according to level of stress resistance (10 and 12 athletes respectively). The variability of heart rate is a more objective and informative analysis which given possibilities of estimate of states of autonomic regulation of athletes. In our study we used the classic approach for analysis of variability of heart rate which recommend the European Association of Cardiologist and North American Association of rhythmology and electrophysiology. Were used the cardiac monitor «Polar RS800CX» for studied of heart rate variability [13]. The parameters of autonomic regulation of heart rate and results of spectral analysis in athletes were registered. The received data was calculated via support of statistical program «Kubios HRV».
The results of autonomic regulation of heart rate in excellent athletes with different level of stress resistance are present in Table 1 The data of(Table 1) are showed the presence of statistical changes between both groups of athletes for heart rate and average duration of RR-intervals (NN). Received result indicates on prevalence of activation of parasympathetic part of autonomic nervous system in athletes of high level of stress resistance. This accompanied by bradycardia (Table 1). The results are shown that in excellent wrestlers with high level of stress resistance the variables of STD RR and pNNxx are reliable increased for concerning to wrestlers with average level of stress resistance. This fact indicates about easing of level of tension of autonomic regulation of heart rate to sinus node. Thus, the study of statistical parameters of variability of heart rate the observe about link between level of stress resistance and peculiarities of autonomic regulation in excellent wrestlers. The study is revealed that the increasing of level of stress resistance related with improving the system of autonomic regulation of heart rate. This reflected by relaxation of level of tension for reason of activation of parasympathetic link of autonomous nervous system. Apart from were showed of bradycardia of athletes with high level of stress resistance.
Table 1: Medians of variables of autonomic regulation of heart (n=22). rate of excellent wrestlers with different level of stress resistance
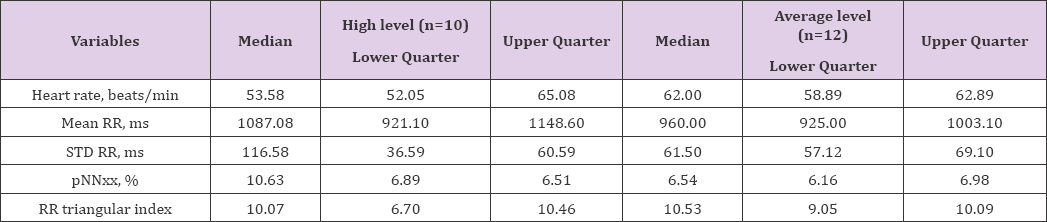
Note: * - p < 0.01, comparing with the group of average level of stress resistance.
Table 2: Medians of variables of spectral characteristics of heart rate variability of excellent wrestlers with different level of stress resistance (n=22).
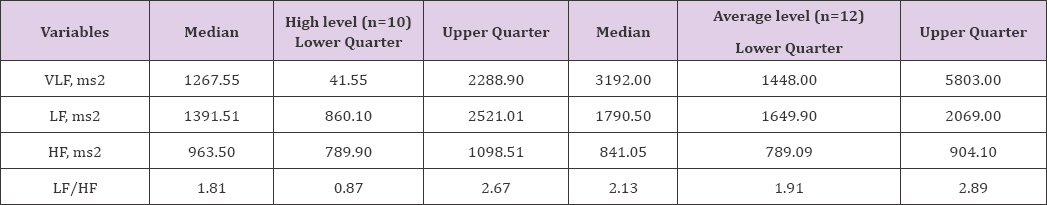
Note: * - p < 0.01, comparing with the group of average level of stress resistance
The variables of spectral characteristics of variability of heart rate in excellent wrestlers with different level of stress resistance presented in Table 2. The data of Table 2 showed the difference between both groups of athletes of stress resistance level by all of parameters of spectral heart rate analysis. Significant more increasing values of VLF and LF parameters in athletes with Average level of stress resistance are shows on activity of central centers of heart rate regulation and influence of sympathetic link of autonomic nervous system to sinus node of heart (Table 2). Analogical dynamics are observed for parameter of vegetative balance (LF/HF). Bigger meanings of LF/HF in athletes with average level of stress resistance for concerning to athletes of high level of stress resistance indicates the amplification of sympathetic and weakening of parasympathetic link of autonomic nervous system (Table 3). The parameters of heart rate variability [11] of excellent wrestlers with different level of stress resistance are present in Table 3. This analysis showed that more significant meanings of Mo RR in athletes with high level of stress resistance indicates on activation of humoral (parasympathetic) regulation of sinus node of heart (Table 3). The same conclusion we can be done for parameters of variation of cardiointervals (D RR). The results indicate that values of D RR in athletes of high level of stress resistance significant bigger for comparison of athletes of average level of stress resistance (Table 3).
Table 3: Medians of parameters of heart rate variability (for R.M. Baevsky, 2004) of excellent wrestlers with different level of stress resistance (n=22).
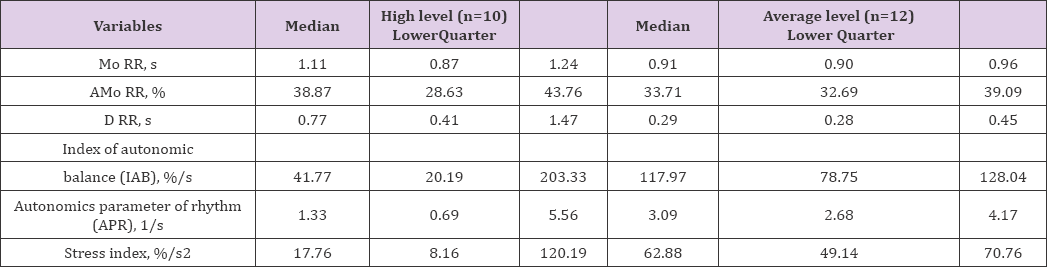
Note: * - p < 0.01, comparing with the group of average level of stress resistance
This fact show about increasing of level of heart rate variability for reason of parasympathetic activity of autonomic nervous system in athletes with high stress resistance level. The changes of index of autonomic balance (IAB) in athletes are indicates that the balance between both parts of the autonomic nervous system system related with stress resistance. The meanings of IAB are reducing in athletes of high level of stress resistance (Table 3). These results view about increasing of activity of parasympathetic tone of the athletes. The vectors of changes of index of autonomic balance (IAB) and autonomics parameter of rhythm (APR) coincides (Table 3). From point of view of conception of RM Baevsky [11]. the heart rate regulation is due to activity of central and autonomic contours of regulation. The centralization of heart rate regulation related with increasing of tension of regulation mechanism. Autonomy conversely is characterized by decline of level of tension of mechanisms of heart rate regulation. The reliably different between groups of athletes for stress index parameter are show of easing of level of tension of autonomic regulation and centralization of heart rate regulation with increasing of stress resistance (Table 3).
Thus, revealed the links between level of stress resistance and tension of autonomic regulation of heart rate in excellent athletes. Were show that in athletes with high level of stress resistance is more variability of heart rate for through activation of parasympathetic and humoral part of regulation of autonomic nervous system [1]. Observed data view the stress tolerance link with develop of autonomic nervous system and balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of heart rate regulation. To study the mechanism of the adaptive process of stress resistance we consider the two-loop model of cardiac rhythm control in the context of control theory [14]. Cardiac sinus node is the controlled object in this case. Control unit is represented by the central control loop [1] (Figure 1).
Training process appears in the role of the input relationship between the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system (Figure 1). Output coordinates of the controlled object vary in response to control signal variations. The functioning of this cardiac rhythm control model in intensive muscular activity depends on the input action [14]. A linearly increasing psychical load, with the change of the system to a new function level, increases the tension in the regulatory mechanisms. The adaptive process is characterized by the fact that control action is generated by the input signal values (perturbations), [1]. Thus, the adaptive process originated at prompt adaptation to training activity corresponds to the "feed-forward" type of control. The adaptive processes of stress resistance under condition of intensive emotional activity were found proceed with a switch to a new level of the organism regulation, [1]. This change to the new control level during intensive psychical activity is accompanied by reinforcement of intrasystem relation, especially pronounced in persons with a low level of stress preparedness. In case of a prompt adaptation to an intensive psychical activity, the organism regulation executed according to the feed forward principle, [1].
The increasing of level of stress resistance related with improving the system of autonomic regulation of heart rate in excellent athletes. This reflected by relaxation of level of tension and activation of parasympathetic part of autonomous nervous system. Were revealed the bigger meanings of LF/HF in athletes with average level of stress resistance for concerning to athletes of high level of stress resistance indicates the amplification of sympathetic and weakening of parasympathetic link of autonomic nervous system. The athletes with high stress resistance level has high of level of heart rate variability and low of centralization of heart rate regulation for compared to athletes with average level of stress resistance [15-19].


